Common Core Ontologies
What is CCO?
The Common Core Ontologies (CCO) is suite of eleven ontologies which, collectively, comprise a mid-level ontology. CCO - initiated by CUBRC, Inc. in 2010 under an IARPA Knowledge Discovery and Dissemination grant - is widely-used in defense and intelligence sectors to support data standardization, interoperability, reproducibility, and automated reasoning across numerous domains. Accordingly, CCO development and application was, for many years, conducted without much transparency. As of 2017, however, CCO has been available under a BSD-3 license with a public GitHub repository open to collaboration. Making CCO publicly available has led to significant increase of interest in CCO development. For example, in 2022 the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) P3195 Standard for Requirements for a Mid-Level Ontology and Extensions working group initiated a review of CCO to become the first mid-level ontology standard. More recently, in 2024 CCO was endorsed as a “baseline standard” for all formal ontology development across the Department of Defense and Intelligence Community.
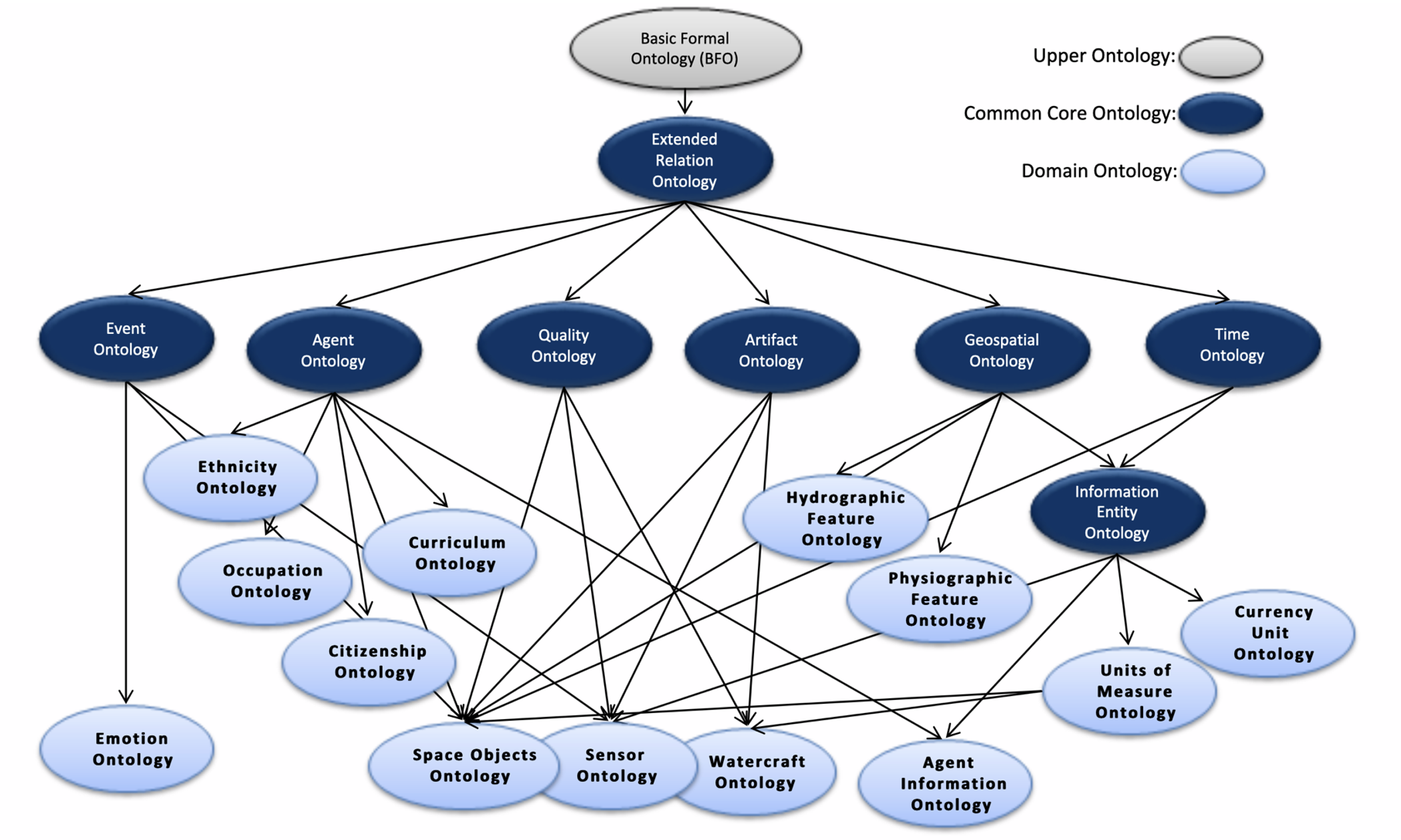
The Common Core Ontologies (CCO) are built on top of the Basic Formal Ontology (BFO) and provide a mid-level layer of ontological terms that bridge between BFO's top-level categories and domain-specific ontologies. This hierarchical relationship is illustrated in the diagram above, where CCO serves as an intermediary layer between BFO and various domain ontologies.
CCO consists of eleven ontologies:
- Geospatial Ontology: An ontology whose scope is the representation of sites, spatial regions, and other entities, especially those that are located near the surface of Earth, as well as the relations that hold between them.
- Information Entity Ontology: An ontology whose scope is the representation of generic types of information as well as the relationships between information and other entities.
- Event Ontology: An ontology whose scope is the representation of processual entities, especially those performed by agents, that occur within multiple domains.
- Time Ontology: An ontology whose scope is the representation of temporal regions and the relations that hold between them.
- Agent Ontology: An ontology whose scope is the representation of agents, especially persons and organizations, and their roles.
- Quality Ontology: An ontology whose scope is the representation of attributes of entities, especially qualities, realizable entities, and process profiles.
- Units of Measure Ontology: An ontology whose scope is the representation of standard measurement units that are used to measure various attributes of entities.
- Currency Unit Ontology: An ontology whose scope is the representation of currencies that countries issue and use.
- Facility Ontology: An ontology whose scope is the representation of buildings and campuses that are designed to serve some specific purpose and are common to multiple domains.
- Artifact Ontology: An ontology whose scope is the representation of artifacts that are common to multiple domains, along with their models, specifications, and functions.
- Extended Relation Ontology: An ontology whose scope is the representation of the relations that hold between entities at the level of the mid-level Common Core Ontologies.
Each of these ontologies extends BFO's top-level categories while providing more specific terms that can be used across multiple domains. This mid-level approach allows for:
- Standardized terminology across different domains
- Improved interoperability between systems
- Reduced redundancy in ontology development
- Consistent representation of common concepts
- Better support for automated reasoning
Below is a list of publications about CCO: